Rail Authority officials say first rides for travelers will be ready by 2031
![]()

By Marty Cheek
The San-Jose-to-Merced stretch of the California High-Speed Rail project got a green light last month.
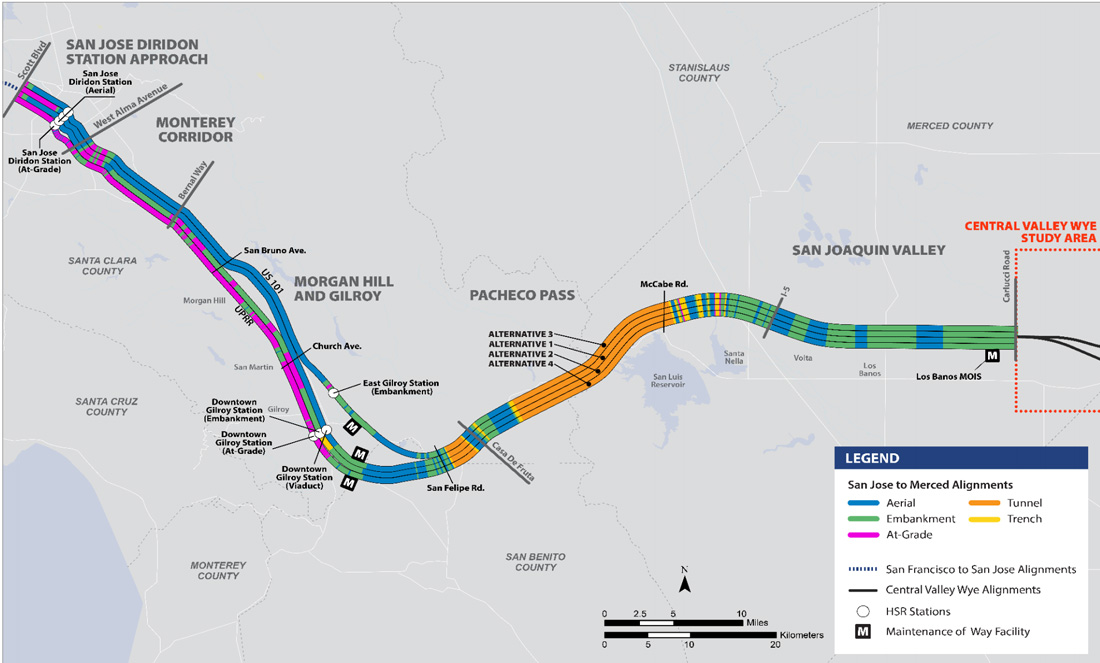
The Rail Authority’s board of directors unanimously approved the environmental impact report at the April 28 meeting. They chose the Alternative 4 route, which passes through downtown Gilroy.
 The 90-mile Alternative 4 route, which, if built, will connect existing construction in the Central Valley to the Bay Area by cutting through Pacheco Pass. Trains will stop at a massive transit center in the southern end of downtown Gilroy.
The 90-mile Alternative 4 route, which, if built, will connect existing construction in the Central Valley to the Bay Area by cutting through Pacheco Pass. Trains will stop at a massive transit center in the southern end of downtown Gilroy.
From there, the route will follow Caltrain tracks along the east side of downtown Gilroy and downtown Morgan, heading north to Diridon Station in San Jose, and then along the Peninsula to the Salesforce Transit Center in San Francisco.
“The High-Speed Rail Authority is saying today that the first ride on that high-speed rail will be ready in 2031, which would be fantastic,” said Gilroy Mayor Marie Blankley. “I just think that may be a little optimistic.”
She was told by the authority that work will start on the transit center in two or three years. If completed, the transit center will be a major transportation hub along the 380-mile line from San Francisco to Los Angeles, impacting the city’s economy by bringing people here for recreation.
“It’s going to be transformative. It means we have rail and bus service in all directions to all of our adjacent counties,” Blankley said. “And I just think that is a major advantage for people not only living here and going to work but to those wanting to come here and stay here and play here.”
 At this time in the process there is a high degree of uncertainty of the direct economic benefits to the South Valley from HSR, said Morgan Hill Chamber of Commerce CEO Nick Gaich who is co-owner of downtown vegan restaurant Craft Roots.
At this time in the process there is a high degree of uncertainty of the direct economic benefits to the South Valley from HSR, said Morgan Hill Chamber of Commerce CEO Nick Gaich who is co-owner of downtown vegan restaurant Craft Roots.
“What is disappointing is the HSR Board did not incorporate Morgan Hill’s repeated advocacy efforts for grade separations at two of our main intersections, East Dunne, and Tennant (avenues),” he said in an email. “This raises questions and concerns regarding public safety, emergency service response times, daily traffic flow, and noise abatement mitigation efforts.”
It’s incumbent Morgan Hill city leadership, the business community, and the residents stay engaged in the HSR conversation and advocate the needs of the community, he stressed.
“Without question, high-speed rail will change the face of Morgan Hill when fully built and operational,” he said. “The Chamber of Commerce will continue to serve as an advocate for our members and community as the HSR process continues to move forward.”
The EIR certification moves the project section closer to being “shovel ready” for when funding becomes available, said Rail Authority CEO Brian Kelly.
“We look forward to continued collaboration with our federal, state and local partners to advance the project in Northern California,” he said.

Courtesy California High-Speed Rail
Gilroy Station concept illustration
East of Gilroy, the alignment includes more than 15 miles of tunnels through the Pacheco Pass in the Diablo Range. The board will consider certification for the final environmental document for the San Francisco to San Jose project section this summer.
The system will make the trip from Fresno to San Jose in just one hour, compared to three hours by car today.
“Completion of this critically important high-speed rail project helps the state expand economic opportunity and affordable housing, two critical goals for all of us,” said San Jose Mayor Sam Liccardo in a press release.
Voters approved Proposition 1A in November 2008, a nearly $10 billion bond to begin construction on the initial leg of the 380-mile railroad’s network. Originally, the project was budgeted at $33 billion in 2008 dollars and the hope for funding was money would come from federal grants and private investments. The 2008 business plan projected construction for the entire project would be completed by 2030.
 Since voters approved the bond, the project has been plagued by escalating costs and delays. In February, the project’s estimated total cost was projected at $105 billion with no secure financing plan and no significant investment of private funds.
Since voters approved the bond, the project has been plagued by escalating costs and delays. In February, the project’s estimated total cost was projected at $105 billion with no secure financing plan and no significant investment of private funds.
The costs of the major Pacheco Pass segment as well as other mountain crossings in the southern region of the state are not yet known and could add significantly to the final price tag of the project, experts say.
As required by the proposition the authority is legally required to design its system to have trains travel from Los Angeles to San Francisco in two hours and 40 minutes.
Rail experts believe it’s unlikely trains will ever meet that trip time in actual operations. Slowing trains through communities from 220 miles an hour to 110 miles an hour will lengthen the trip time.
Despite the project’s challenges, most Californians support it. Results of a U.C. Berkeley poll in April showed 56 percent of voters supported continuing the project, while 35 percent opposed continuing it.






